How to Improve Your Soil: 5 Simple Techniques
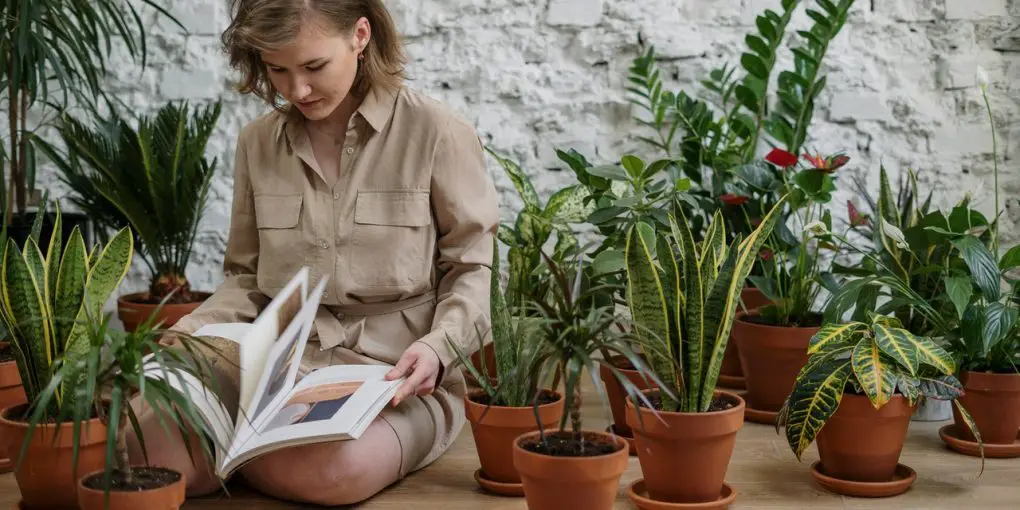
Healthy ground is crucial for all farming endeavors, whether you’re cultivating blossoms or raising crops for industrial use. It lessens the likelihood of disease occurrence and enhances plant development. Thanks to contemporary technological advancements, it’s possible to improve the quality of soil significantly, even if it starts off poor. Nowadays, remarkable outcomes can be attained domestically without the need for substantial monetary investment.
Why Does Organic Matter Matter?
Organic matter is vital for gardening and farming. It improves soil structure and provides crops with nutrients. It also serves as a food source for organisms living in the earth. The dirt itself receives nutrient-rich humus. Moreover, organisms tunnel it, facilitating air and moisture penetration. As a result, it is possible to enhance the clay soil’s structure providing better plant roots’ growth. At the same time, organic matter in lightweight and sandy soil compacts it and allows it to keep more moisture and nutrients.
5 Simple Techniques
There are different ways to improve the soil. Here are 5 of the simplest ones suitable for different types of home farming. They can be used in small gardens for growing vegetables or on flower beds. All techniques do not require special financial costs and are suitable for almost everyone.
Test your soil
When you add fertilizers and organic matter to the ground, analyze changes in soil chemistry. If it has improved but not balanced, you will be able to define how to achieve the best option. By testing the ground, you will understand how it should be in its natural state, acidic or alkaline. A well-balanced pH standpoint will contribute to better plant adaptation.
Use cover crops
Cover crops are beneficial for soil improvement. They grow densely on top of each other, forming a living mulch. It decreases earth erosion and the weeds’ number. Moreover, there are winter and summer cover crops so that you can use them at any time of the year. Also, you can use these cultures as “green manure.” Clover, beans, oats, and buckwheat can be distinguished among such crops. They deliver the dirt with essential nutrients. For example, nodules on the leguminous plants’ roots are inhabited by bacteria that convert nitrogen into a valuable form for plants. When the roots of dead legumes decompose, the residual nitrogen is released to farm the crops. This technique is called nitrogen fixation.
Add compost
Garden and kitchen waste can be an excellent fertilizer for the soil. Compost retains moisture in the ground and fills it with nutrients and organic matter. Such fertilizers are suitable for individual plants, using a minimum amount of kitchen waste. For example, you can fertilize the garden flowers with coffee grounds or eggshells. If your compost stocks are not enough, you can buy them in specialized stores.
Mulch
Mulch is a manure or compost layer covering the topsoil. Many experts call this method one of the most useful in maintaining plant health. Mulch retains moisture in the soil and, as it decomposes, allows nutrients to penetrate the soil.
Provide air and water
Air and water are vital to plant root health and beneficial microbes. Their reserves are concentrated in the so-called microenvironments. Soil compaction or over-tillage can destroy them. Because of this, the soil and plants do not receive nutrients water in full. Also, it promotes the growth of weeds, which can also cause severe damage to crops.
There are different ways to create an optimal environment. Here are some options:
- grow plants on raised beds;
- make beds at such a distance that you have access from all sides;
- try to use hand tools to prepare the beds;
- apply compost to compacted soil.
These tips need to be adjusted depending on the plants grown. For example, flowers and vegetables need spreading 2 inches of compost to a depth of 8 inches. For trees and shrubs, the volume is more extensive – 2 inches of compost to a depth of 12 inches.
The listed techniques are suitable for households of various types. They do not require much financial investment. All you need are internal resources, for example, using garden and kitchen waste as fertilizer. All of them must be environmentally friendly, so you maintain healthy soil and crops along with improved plant growth.